Use of Tilt-Shift Lens for Architectural and
Landscape Photography
What is Tilt-Shift Lens?
Tilt-shift lens can change the optical axis directly. If offers two functions, namely Shift function that alters the extracted area of the image circle and Tilt function that changes the depth of field. This article will discuss mainly on how the Shift function can help in architectural and landscape photography.
The Principle of Shift Correction
The image created after the light entering the lens is circular, and this is what we call the image circle. The rectangular photo we see is extracted from the image circle. The Shift function works by allowing the extracted area to move on the image plane, thus changing what part of that circular image to capture without altering the camera’s position and angle of view. Normally a tilt-shift lens can only move along one axis, and we can change the direction of movement by rotating the lens.
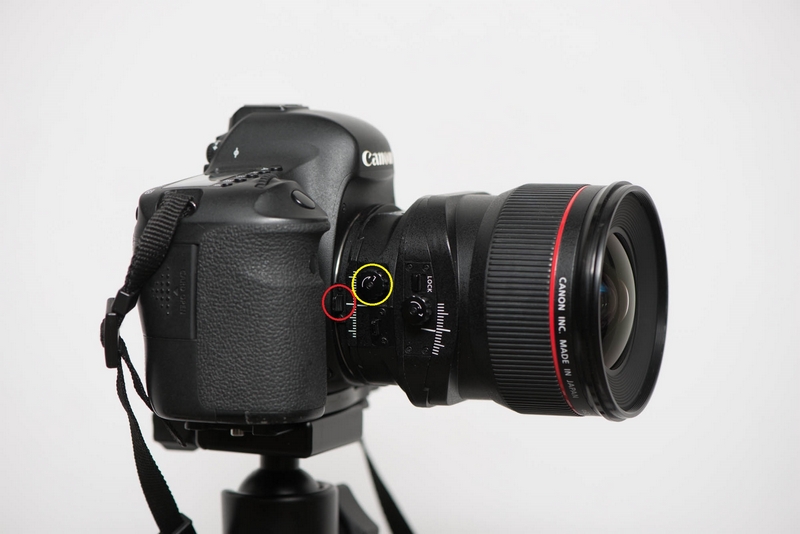

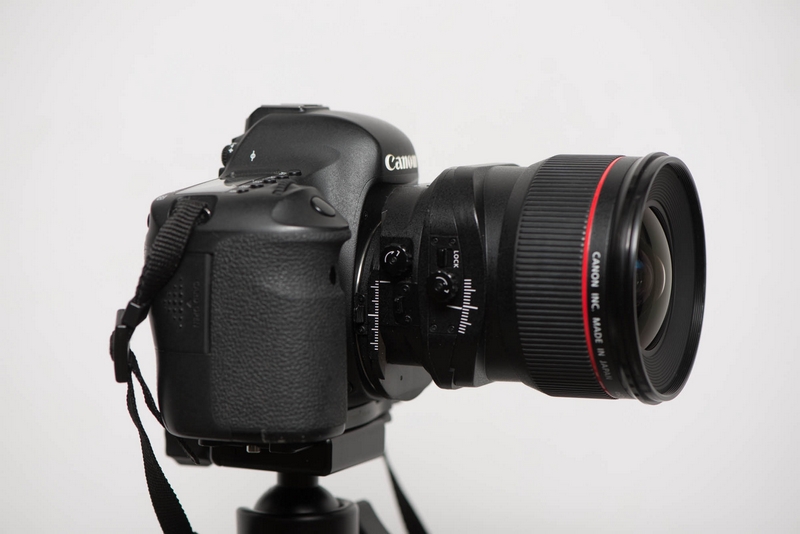
Turn the yellow-circled button to control the degree of tightness of the Shift function; press the red-circled button to rotate the lens
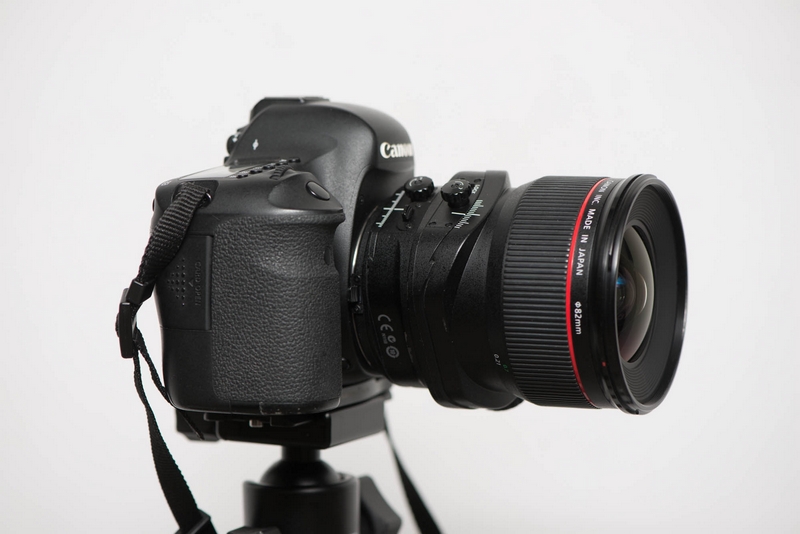

By pressing the red-circled button to rotate the lens, you can change the shift axis
Correction of Building Distortion
As most buildings are taller than the photographer, we need to angle the camera upward to get the entire building in the shot when shooting with a normal lens. Since the image sensor is not parallel to the building, the bottom of the building will appear wider and bigger than the top. If we take picture from a horizontal level, the top of the building will be excluded in the composition as a result of the height.

When we angle the camera upward to take shot of the building, perspective distortion will occur
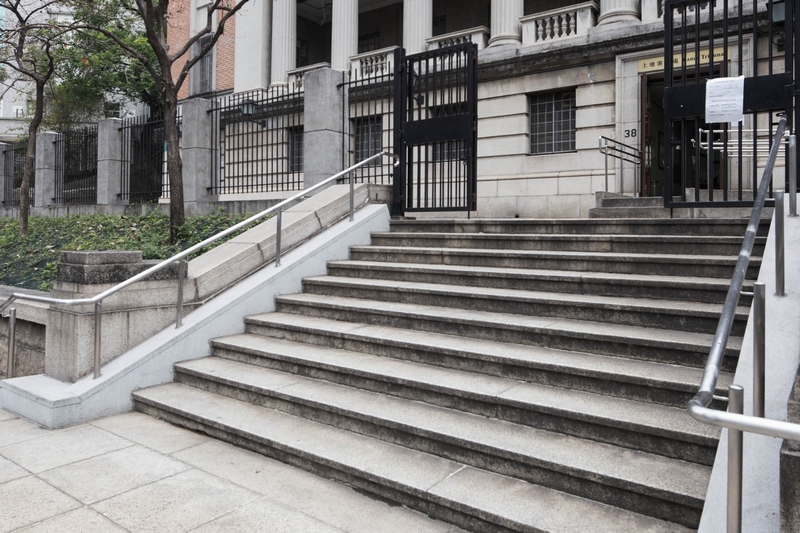

When we shoot horizontally from the ground, we cannot capture the entire building due to its height
This problem can be resolved by using the Shift function of a tilt-shift lens. Simply position your camera so that the image plane is parallel to the building, and shift the lens up for undistorted images.

Shift the lens vertically with the Shift function
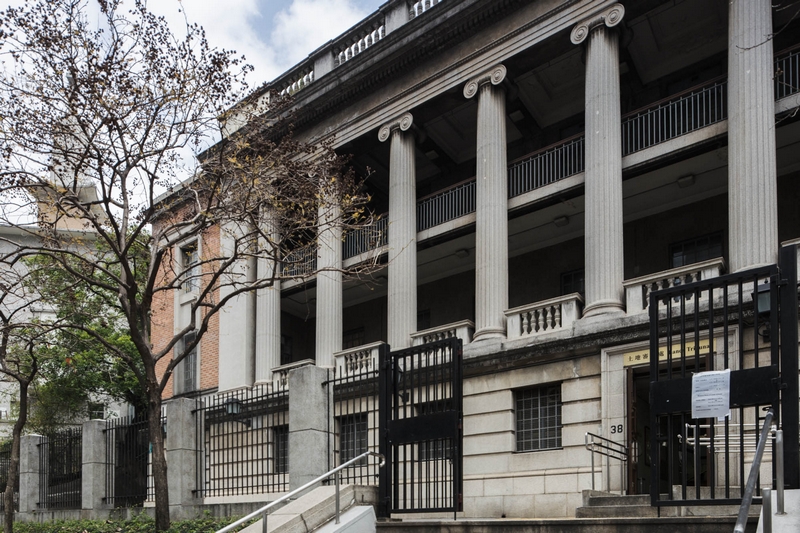

The distortion is corrected
Taking Panoramic Photos
Nowadays, most cameras or even smart phones offer built-in panoramic mode. This is done by turning your camera or phone around a vertical axis to capture multiple images that will be stitched to become a panoramic photo by internal programme. This makes taking panoramic photos easy, but the digitally composited image will be vastly distorted and is not pleasing to the eyes.
A better way to create panoramic photo is by using the Shift function of a tilt-shift lens. With a few post-editing steps, we can create optically composited panoramic photo with minimal distortion. First, mount your camera on a tripod. Then take images with the Shift function from the leftmost to the rightmost position (usually three photos from the left, middle and right) and composite the images together in post-editing to create a panoramic photo that shows a wider perspective.
A better way to create panoramic photo is by using the Shift function of a tilt-shift lens. With a few post-editing steps, we can create optically composited panoramic photo with minimal distortion. First, mount your camera on a tripod. Then take images with the Shift function from the leftmost to the rightmost position (usually three photos from the left, middle and right) and composite the images together in post-editing to create a panoramic photo that shows a wider perspective.

Mount your camera on a tripod and take three photos from the left, middle and right
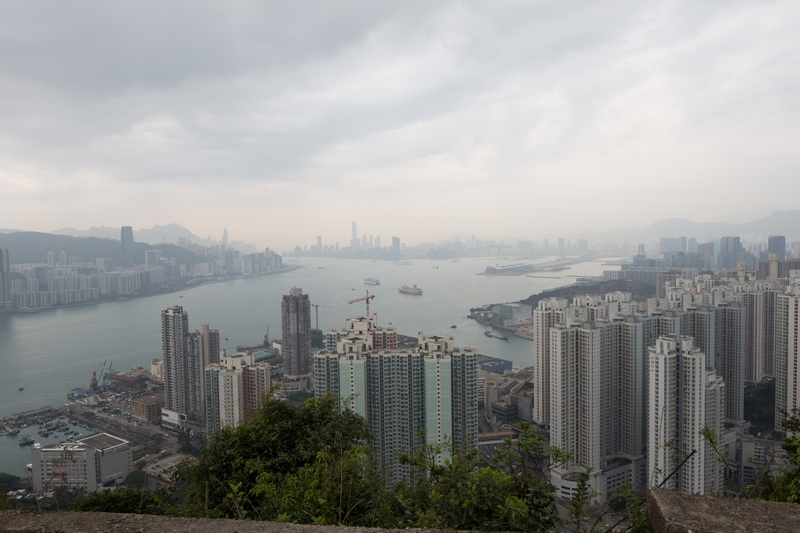
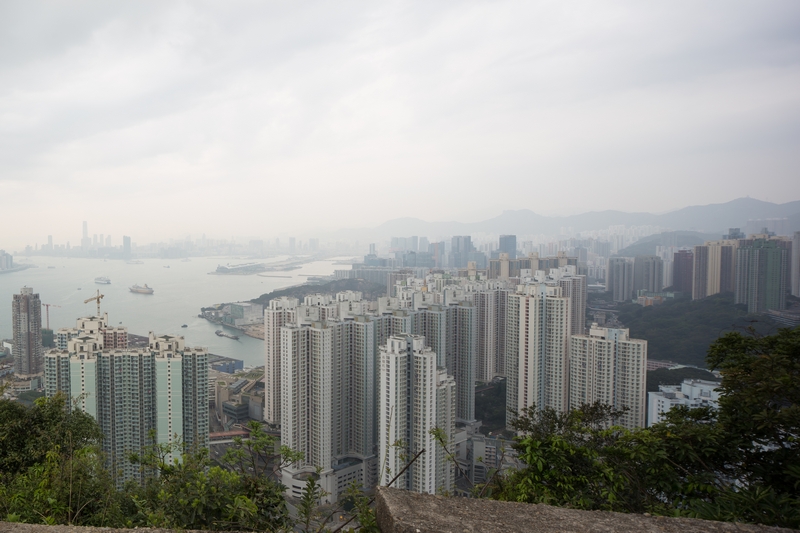


Post-Editing Procedure
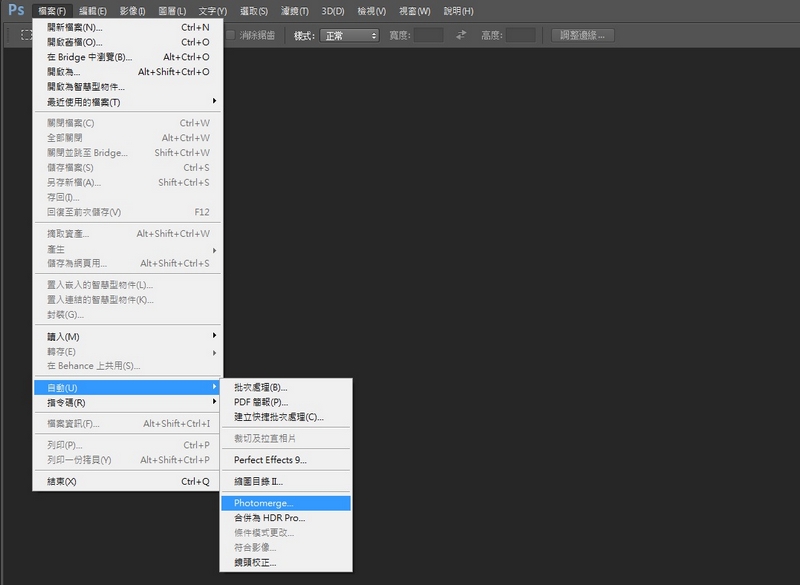
Launch Photoshop without opening the image files. Click File→Auto→Photomerge
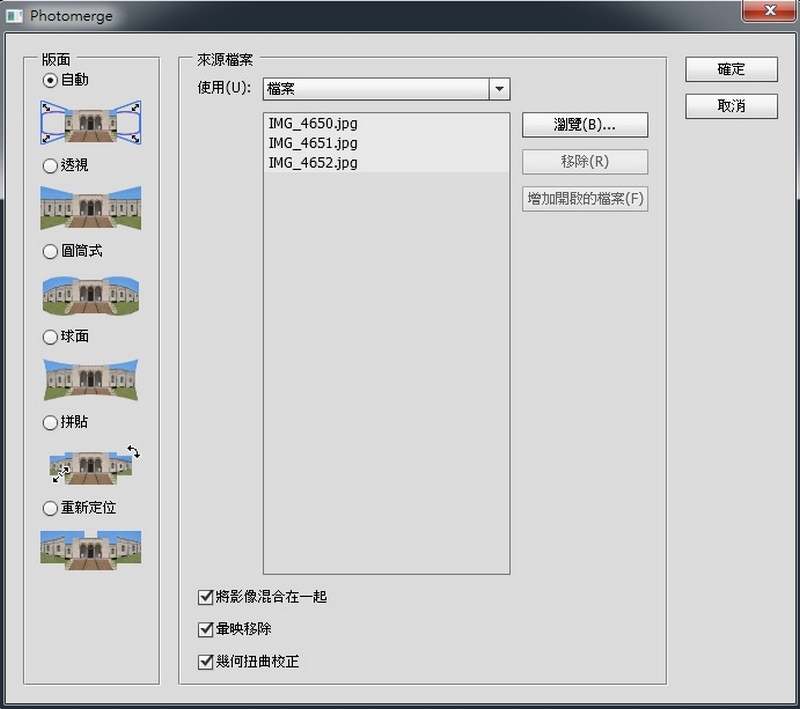
Select Auto and the images to merge. Check the three boxes on the bottom and click Confirm

Photoshop will merge the images automatically and you can see the final image

Edit the final image after merging
We can tell from the final image that a panoramic photo created this way is distortion-free, although the field of view may not be as wide as the built-in panoramic mode. Tilt-shift lens is very useful, especially for taking photos of architecture and landscape. Do try it out!
Tilt-shift lens also comes in various focal lengths. For example, Canon’s tilt-shift lens series offers choices of 17mm, 24mm, 45mm, 90mm and more. The wider the lens, the better it is for panoramic shooting as it offers a wider field of view. Relatively, the longer the focal length, the more apparent the depth of field is, leading to more obvious depth of field change when using the Tilt function.
Tilt-shift lens also comes in various focal lengths. For example, Canon’s tilt-shift lens series offers choices of 17mm, 24mm, 45mm, 90mm and more. The wider the lens, the better it is for panoramic shooting as it offers a wider field of view. Relatively, the longer the focal length, the more apparent the depth of field is, leading to more obvious depth of field change when using the Tilt function.




